Features
Greenhouse Effect and its Impact on Climate Change
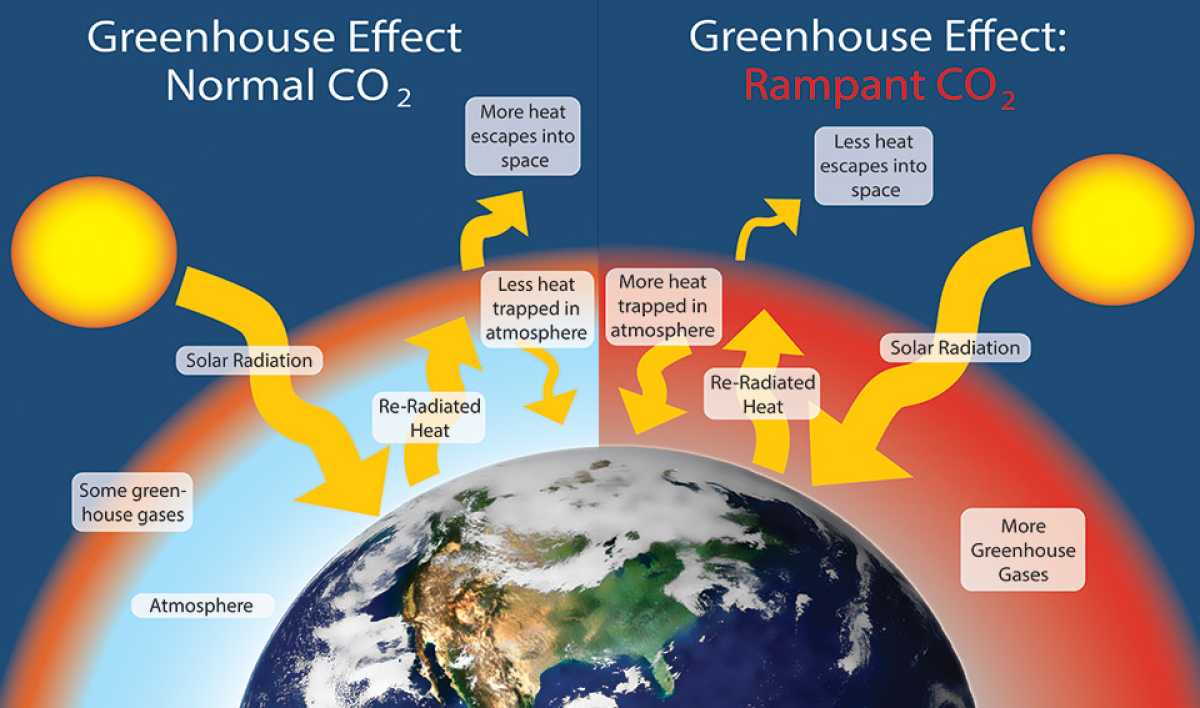
The greenhouse effect is a vital concept in understanding the delicate balance of Earth’s climate. It plays a pivotal role in the ongoing global conversation about climate change and its consequences. In this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into the greenhouse effect, greenhouse gases, their definitions, causes, and effects, and how they contribute to global warming and climate change. We will also explore the difference between the greenhouse effect and global warming while providing a clear explanation of these complex topics.
Greenhouse Effect: A Fundamental Overview
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface. It occurs when certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere trap heat from the sun, preventing it from escaping back into space. These gases, known as greenhouse gases, include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and water vapor (H2O), among others. The greenhouse effect is essential for maintaining a habitable temperature on our planet, as it keeps the Earth’s surface at an average temperature of about 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius). Without this effect, Earth would be too cold to support life.
Defining Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases are central to understanding the greenhouse effect. They are any gas in the atmosphere capable of trapping heat. Some of the most common greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone. These gases create an insulating layer around the Earth, which allows sunlight to enter but prevents the escape of heat, leading to an increase in temperature.
Causes of the Greenhouse Effect
The primary cause of the greenhouse effect is the increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere. Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, release significant amounts of these gases. As a result, the concentration of greenhouse gases has risen to levels not seen in millions of years. This enhanced greenhouse effect intensifies the trapping of heat, leading to global warming.
Global Warming and the Greenhouse Effect
Global warming is the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature, primarily driven by the enhanced greenhouse effect. As greenhouse gases accumulate in the atmosphere, they trap more heat, causing the planet to warm. The consequences of global warming are far-reaching and include rising sea levels, more frequent and severe weather events, and the disruption of ecosystems.
Differentiating the Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
While the greenhouse effect and global warming are closely related, they are distinct concepts. The greenhouse effect is the natural process that keeps the Earth’s surface warm, while global warming is the result of an intensified greenhouse effect due to increased greenhouse gas concentrations. In essence, global warming is the outcome of an imbalanced greenhouse effect.
Understanding the Role of Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is one of the most significant greenhouse gases. It is released into the atmosphere through human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation. The excess CO2 in the atmosphere acts like a blanket, trapping heat and causing the Earth’s temperature to rise, contributing to global warming.
Impact of Greenhouse Gases on Climate Change
The excessive accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has far-reaching effects on climate change. It leads to increased temperatures, which, in turn, cause melting ice caps and glaciers, resulting in rising sea levels. Additionally, altered weather patterns and the intensification of natural disasters like hurricanes and droughts are consequences of climate change driven by greenhouse gases.
Preventing the Greenhouse Effect
Preventing the greenhouse effect from worsening is crucial in mitigating climate change. This can be achieved through reducing greenhouse gas emissions by transitioning to clean energy sources, increasing energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable land-use practices. It’s essential to work collectively to reduce our carbon footprint and limit the impact of the greenhouse effect on our planet.
The Significance of Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases are critical to maintaining the Earth’s temperature within a habitable range. They allow us to enjoy a stable climate that supports diverse ecosystems and human life. However, the excessive release of greenhouse gases poses a significant threat to the environment, and we must find ways to balance their concentration in the atmosphere.
Types of Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases come in various forms. The most common ones include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor (H2O). Each of these gases has different heat-trapping abilities and atmospheric lifetimes, contributing to the complexity of the greenhouse effect.
Conclusion
In summary, the greenhouse effect is a natural process that plays a crucial role in maintaining Earth’s temperature. However, the enhanced greenhouse effect caused by the accumulation of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide, is driving global warming and climate change. Understanding these phenomena, their causes, and their consequences is essential for taking action to mitigate their impact on our planet. We must collectively work towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly way of living to protect the future of our planet. The greenhouse effect is a fundamental part of Earth’s climate system, and how we manage it will determine the fate of our planet for generations to come.












