Health
Distinguishing Between Flu and COVID-19 Symptoms: A Guide for the Upcoming Winter Season
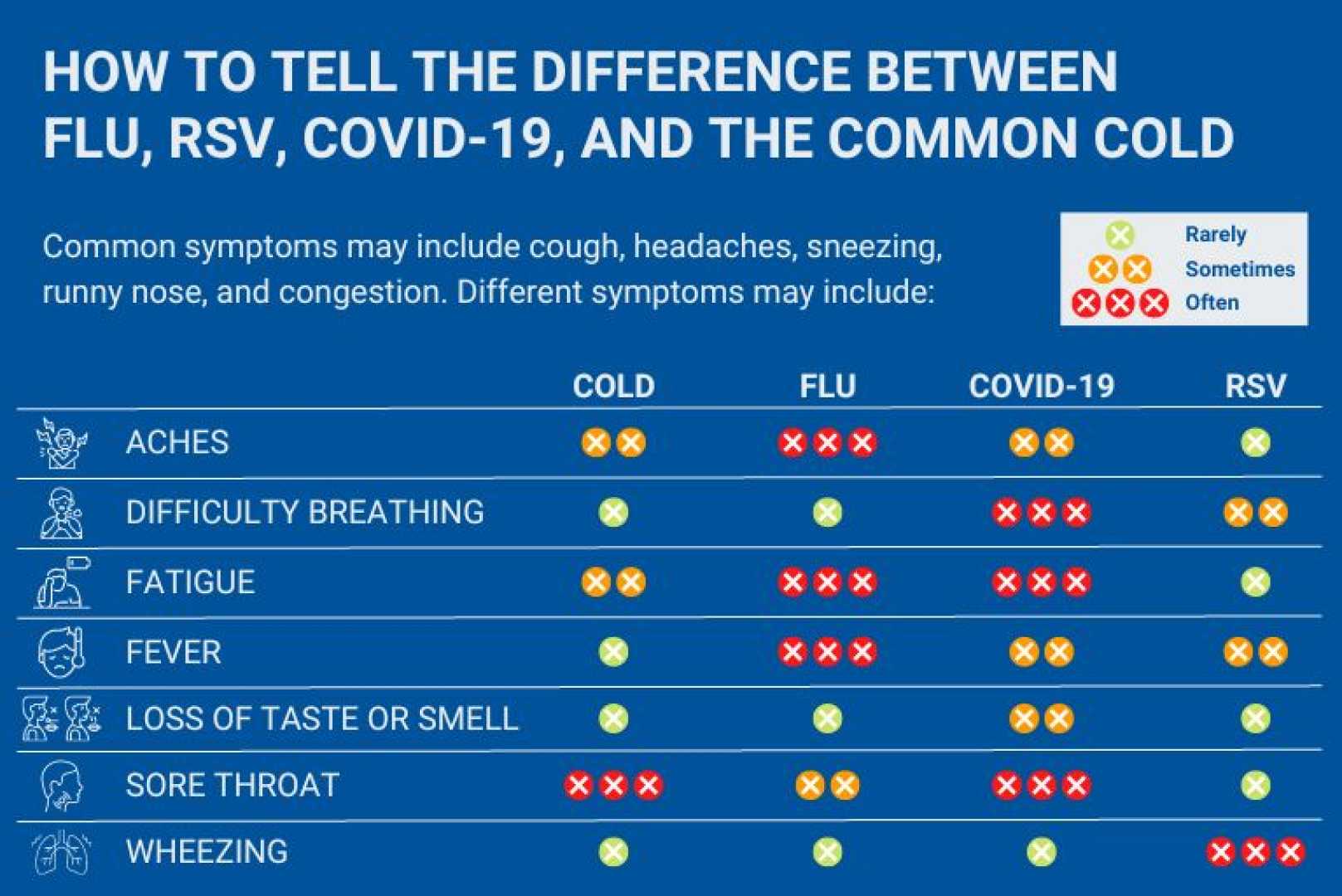
As the winter season approaches, the likelihood of encountering illnesses such as the flu and COVID-19 increases, especially with more people gathering indoors. Distinguishing between the symptoms of these two viruses can be challenging due to their overlap, but there are some key differences and considerations to keep in mind.
Both COVID-19 and the flu share common symptoms, including sore throat, fever, fatigue, muscle aches, and cough. According to Dr. Amesh Adalja, an expert in infectious diseases and a senior scholar with the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, “there is no real way to distinguish COVID-19 from influenza based on clinical symptoms because they overlap so much”.
However, there are slight differences in the timing of symptom onset. Flu symptoms typically appear one to four days after infection, while COVID-19 symptoms may appear two to five days post-infection, and in some cases, can take up to two weeks to manifest.
A notable symptom that was more common during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic but has become less frequent is the loss of taste and smell. This symptom is not typically associated with the flu.
Both viruses cause the most severe illness and lead to complications in similar populations: adults in their 60s and up, and younger people with certain medical conditions. If you are planning to spend time with someone at high risk, it is crucial to err on the side of caution and wait until you are no longer sick to see them face-to-face.
If you are at higher risk, consulting your doctor for a proper diagnosis is essential, as the treatments for flu and COVID-19 differ. Antivirals for either condition should be started immediately upon diagnosis.
In addition to flu and COVID-19, another virus to consider is Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), which can cause mild symptoms in most adults but severe symptoms in older adults and young babies. Vaccines for RSV are now available to protect these vulnerable groups.
Distinguishing between viral infections and allergies is also important. Allergies typically cause itching of the eyes, nose, or top of the mouth, which is not usually common in viral infections. Other symptoms of allergic rhinitis include congestion, sneezing, headaches, and sinus pain.












