Health
Cervical Cancer: The Silent Killer- Understanding the Disease and Its Implications
Actor and model Poonam Pandey, aged 32, tragically lost her battle against cervical cancer on February 2. Her demise has put the spotlight on this deadly disease, which often goes unnoticed until it reaches advanced stages. Early detection of cervical cancer remains a significant challenge in India, resulting in a high death rate.
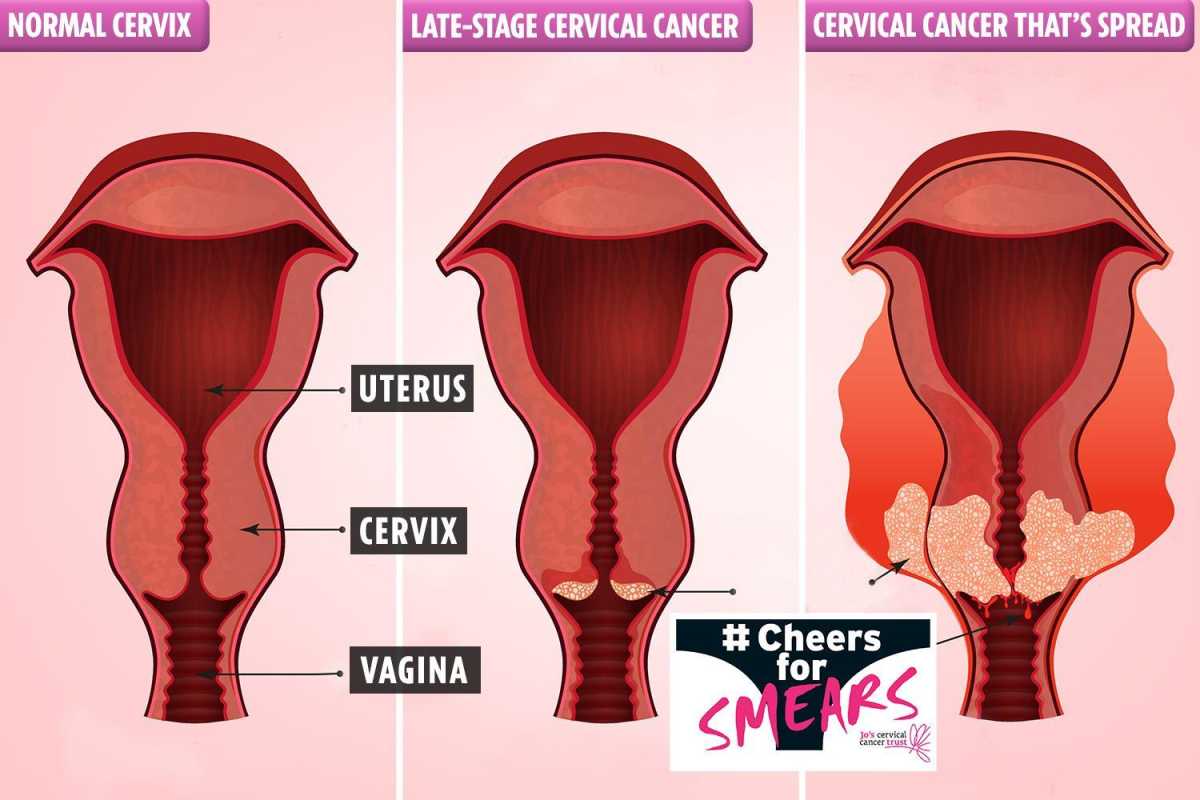
Cervical cancer, primarily caused by the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), affects the cells lining the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. This type of cancer is mainly transmitted through sexual intercourse. Unfortunately, HPV infections rarely cause symptoms, making it challenging to detect and diagnose the disease in its early stages. Symptoms may take years to develop after exposure to an infected person, further complicating early detection.
The World Health Organization (WHO) ranks cervical cancer as the fourth most common cancer in women globally. In 2020 alone, approximately 604,000 women worldwide were diagnosed with cervical cancer, resulting in about 342,000 deaths. Despite its high incidence, cervical cancer is highly treatable if detected early.
The Indian government’s recent push to vaccinate girls in the 9-14 age group against cervical cancer comes as a significant step in preventing the disease. The Union Finance Minister highlighted this initiative during the budget presentation, emphasizing the importance of vaccination for the prevention of cervical cancer. The government announced its plan to evaluate an India-made quadrivalent vaccine for inclusion in the Universal Immunisation Programme (UIP) as a twin-dose regimen for adolescent girls.
Regular screenings and HPV vaccinations play a vital role in preventing and detecting cervical cancer early. Women with weakened immune systems, young mothers, hormonal contraceptive users, smokers, and individuals with other sexually transmitted infections are at a higher risk of developing this condition. Treatment options include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and pain management.
The passing of Poonam Pandey serves as a tragic reminder of the silent killer that is cervical cancer. It is crucial to raise awareness about the importance of regular screenings, HPV vaccinations, and overall women’s health to combat this deadly disease.












