Health
New Research Reveals Alarming Rise in Global Obesity Rates
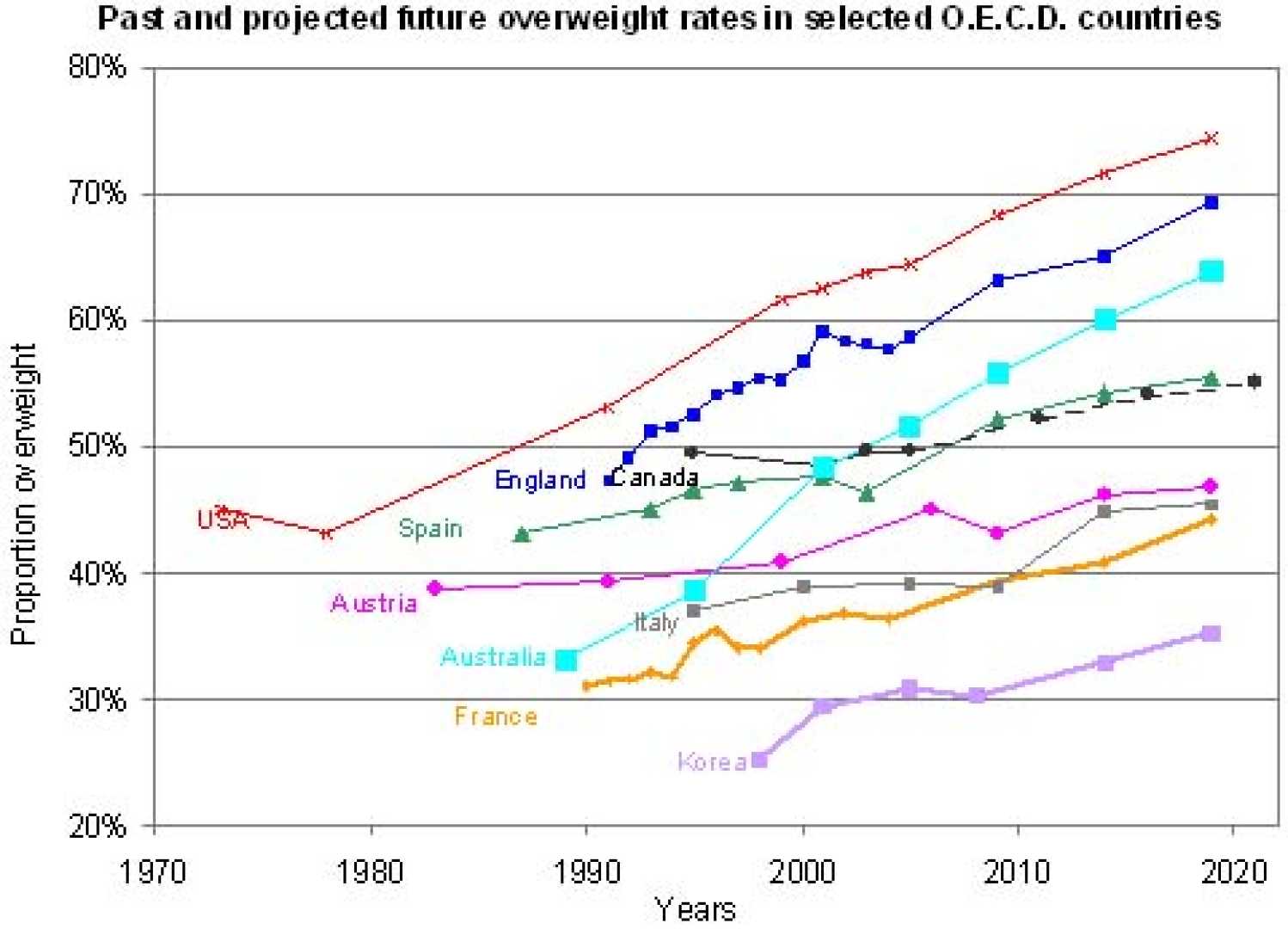
GENEVA, Switzerland — A recent study published by the World Health Organization (WHO) found that global obesity rates have escalated dramatically over the past two decades, prompting urgent calls for public health interventions.
The study, released on November 1, 2023, indicates that nearly 2 billion adults are classified as obese worldwide, with the highest rates observed in North America and parts of Europe. Researchers attribute this alarming trend to factors including poor diet, sedentary lifestyles, and social disparities in access to healthy food.
“Obesity is a complex issue that requires a multifaceted approach,” said Dr. Maria Neira, WHO’s Director for Public Health and Environment. “Governments need to implement policies that promote healthier food choices and encourage physical activity among citizens.”
The research highlights that obesity can lead to serious health issues, including diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and several types of cancer. According to the WHO, the medical costs associated with obesity-related conditions are estimated to reach $2 trillion annually by 2025.
To further illustrate the dramatic increase, the study notes that the prevalence of obesity has nearly tripled since 1975. The highest rates were found in countries like the United States, where over 36% of adults are classified as obese.
“Our planet is facing an epidemic of obesity that affects all demographics and communities,” stated Dr. John Miller, a leading researcher at the Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation. “If we do not take immediate action, we risk the health of entire generations.”
In response to growing concerns, several countries have begun implementing strategies to combat obesity. In recent years, nations such as Mexico and the United Kingdom have introduced sugar taxes and educational programs aimed at reducing junk food consumption.
The WHO recommends increasing food taxes, improving urban planning to encourage walking and biking, and expanding access to preventive healthcare services for underprivileged populations as solutions to combat this crisis.
As nations evaluate their health policies in light of these findings, experts stress the importance of long-term commitment to changing dietary habits and increasing physical activity through community initiatives.
“This issue transcends personal responsibility; it requires a societal shift toward healthier environments,” Dr. Neira added. “Collective action will be essential in reversing this trend.”












