Health
CBD Reduces Alcohol Cravings in Clinical Trial, Study Finds
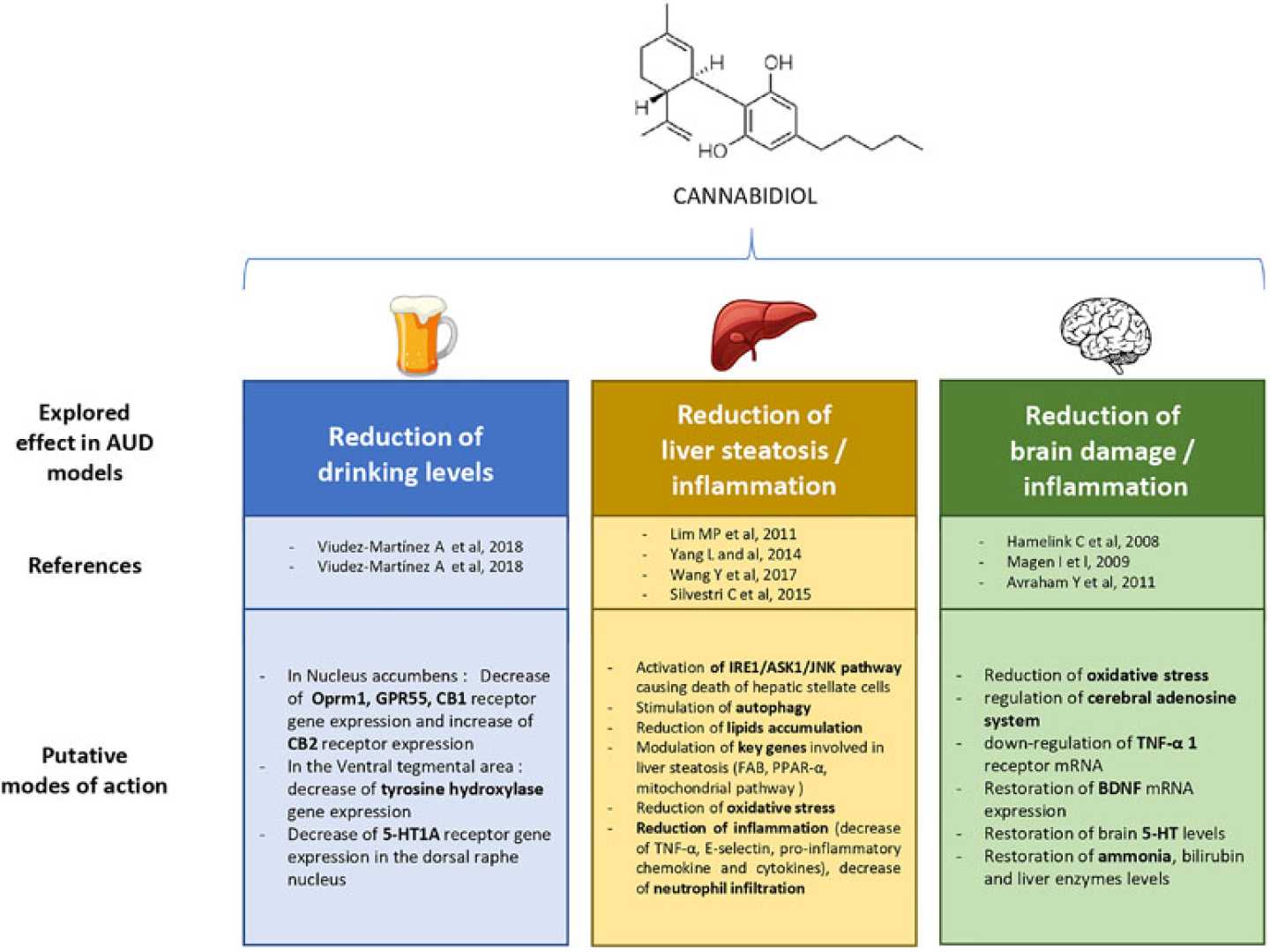
MANNHEIM, Germany — A groundbreaking clinical trial has revealed that cannabidiol (CBD), a non-intoxicating compound derived from cannabis, significantly reduces alcohol cravings in individuals with alcohol use disorder. The study, conducted by researchers at the Central Institute of Mental Health (CIMH), provides the first clinical evidence of CBD’s potential to combat alcohol addiction.
The double-blind, randomized, and controlled trial, published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry, involved 28 participants aged 18 to 60 with mild to severe alcohol-related illnesses. Participants were divided into two groups: one received a single 800 mg dose of CBD, while the other was given a placebo. Researchers then exposed participants to alcohol-related stimuli, such as images of alcohol or a simulated bar environment, to trigger cravings.
Using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), the team measured brain activity in the nucleus accumbens (NAc), a region associated with reward and addiction. Results showed that participants who received CBD reported significantly lower cravings for alcohol compared to the placebo group. Additionally, the NAc was less activated in those who took CBD, suggesting a reduced likelihood of relapse.
“Our study provides initial and clear evidence that cannabidiol can help to reduce the craving for alcohol and change the brain activity associated with addiction,” said Prof. Dr. Patrick Bach, research group leader at CIMH. Scientist Sina Vetter added, “Further research is needed to determine whether these results are broadly applicable and whether the effects of CBD remain stable over time.”
The findings highlight CBD’s potential as a novel treatment for alcohol addiction, a condition that affects millions worldwide and has limited pharmacological treatment options. The research team is now preparing a follow-up study, ICONICplus, to explore the combined effects of CBD and naltrexone, an existing medication for alcohol dependence.
Alcohol-related diseases are among the most devastating global health issues, with high relapse rates even among those receiving standard treatments. The study underscores the urgent need for innovative approaches to address this public health crisis.












