Health
Singapore Scientists Develop mRNA Vaccine Delivery Platform to Enhance Stability
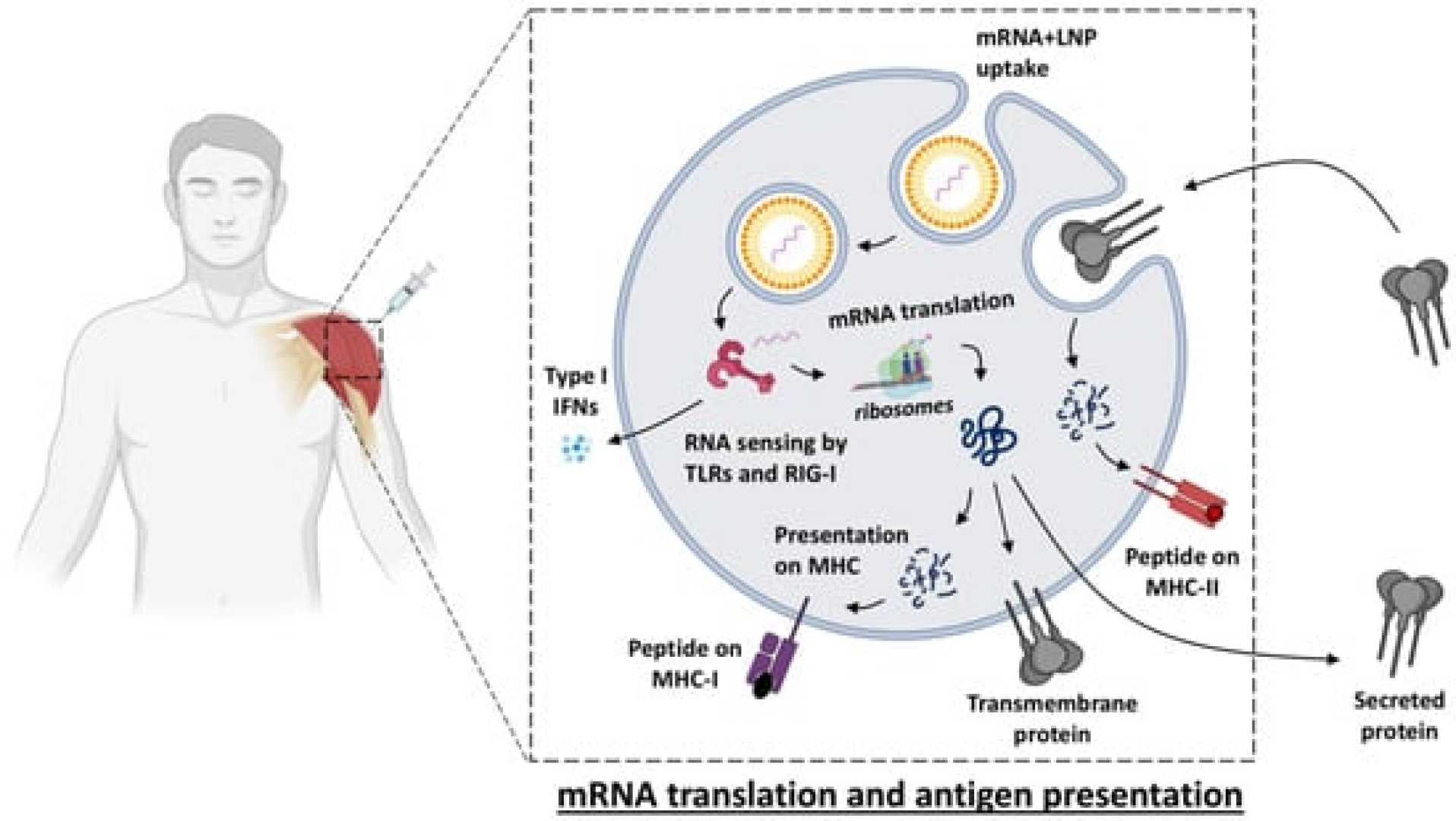
OSLO, SINGAPORE – A team of scientists in Singapore is investigating a new platform designed to improve the stability of mRNA-based vaccines. This research, funded by the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), could enhance global access to these lifesaving vaccines.
The CEPI is providing up to US$2.87 million to ACM Biolabs for preclinical proof of concept of its mRNA delivery technology, known as the ACM Tunable Platform (ATP). The research aims to utilize rabies as a model pathogen in its trials.
The ATP platform offers a significant advantage over traditional mRNA delivery systems, which require ultra-low temperatures for storage. Instead, ATP enables mRNA stability at temperatures of 2-8°C, making it much easier to store and transport these important vaccines.
“Removing the need for frozen storage would make mRNA vaccines significantly easier and cheaper to ship, store and distribute, especially in low-resource settings,” said Kent Kester, Executive Director of Research and Development at CEPI.
Madhavan Nallani, CEO of ACM Biolabs, expressed confidence in the project’s potential. “Our ATP platform is engineered to enhance thermostability, improve immune responses, and ultimately simplify the vaccine distribution process,” he stated.
The ATP technology may not only improve how vaccines are stored and transported but could also provide better immune protection. It is believed that ATP might enhance T cell activation, which is vital for long-term immunity, as well as boosting antibody responses that combat viruses.
CEPI and ACM Biolabs emphasize their commitment to equitable access to the resulting vaccines, aiming to prioritize populations at risk when they are developed further.
This collaboration forms part of a broader effort by CEPI, which has supported the development of over 60 vaccine candidates against high-risk pathogens and aims to compress vaccine development timelines for future outbreaks.












