Health
U.S. Launches $500 Million Universal Vaccine Initiative
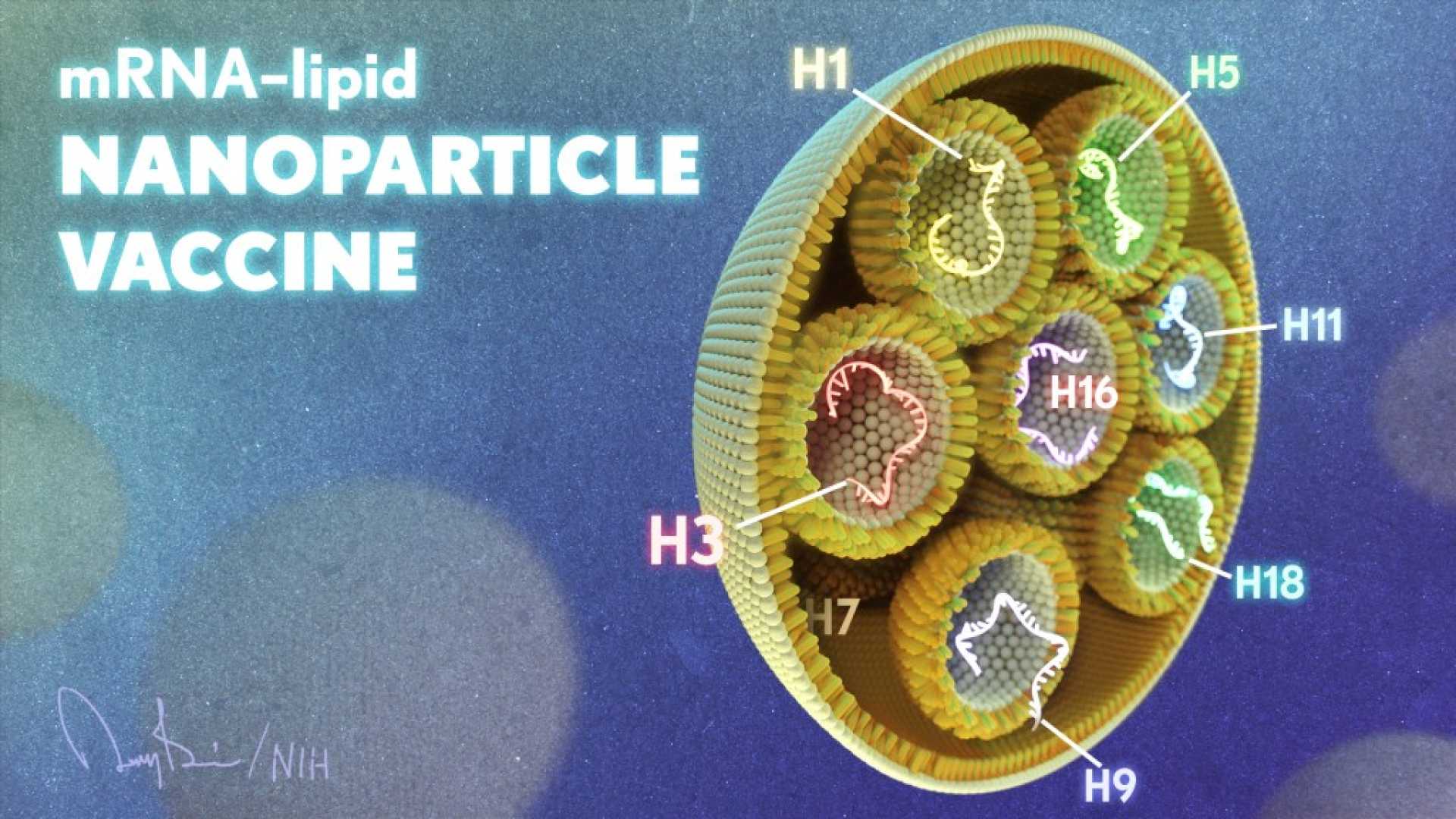
Washington, D.C. — U.S. health agencies announced on Thursday they are investing $500 million to develop a universal vaccine technology aimed at combating multiple strains of viruses like influenza and coronaviruses. This project, referred to as the ‘Generation Gold Standard,’ marks a significant shift in federal funding from COVID-19 projects to broader viral research.
The initiative is led by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). According to reports, clinical trials for a universal flu vaccine are expected to begin in 2026, with a decision from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) anticipated by 2029.
An HHS spokesperson emphasized that this project provides a ‘cost-effective, accountable alternative’ to existing COVID-19 vaccines and treatments. The funding is coming from the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), which typically finances measures designed to protect public health during emergencies.
Government officials expressed surprise at the redirection of funds, which they noted bypassed traditional review processes meant to assess projects based on scientific merit. This funding decision, which came via communications from HHS, has raised questions about the approach to federal research allocation.
This project follows earlier discussions within the NIH regarding pan-coronavirus vaccines. In alignment with the HHS objectives, the goal is to ensure preparedness against a range of viral threats, not just COVID-19.
Robert F. Kennedy Jr., a notable skeptic of vaccines, currently leads the HHS, and he has stated that the initiative ensures that ‘every innovation in vaccine development’ adheres to established standards of science and efficacy. The department plans to explore further vaccine technology options, including COVID-19, using the beta-propiolactone (BPL) approach in their ongoing research.
In summarizing their commitment, HHS officials reiterated their focus on developing in-house vaccines to enhance pandemic preparedness, reflecting a decisive shift in priorities for federal health funding.












